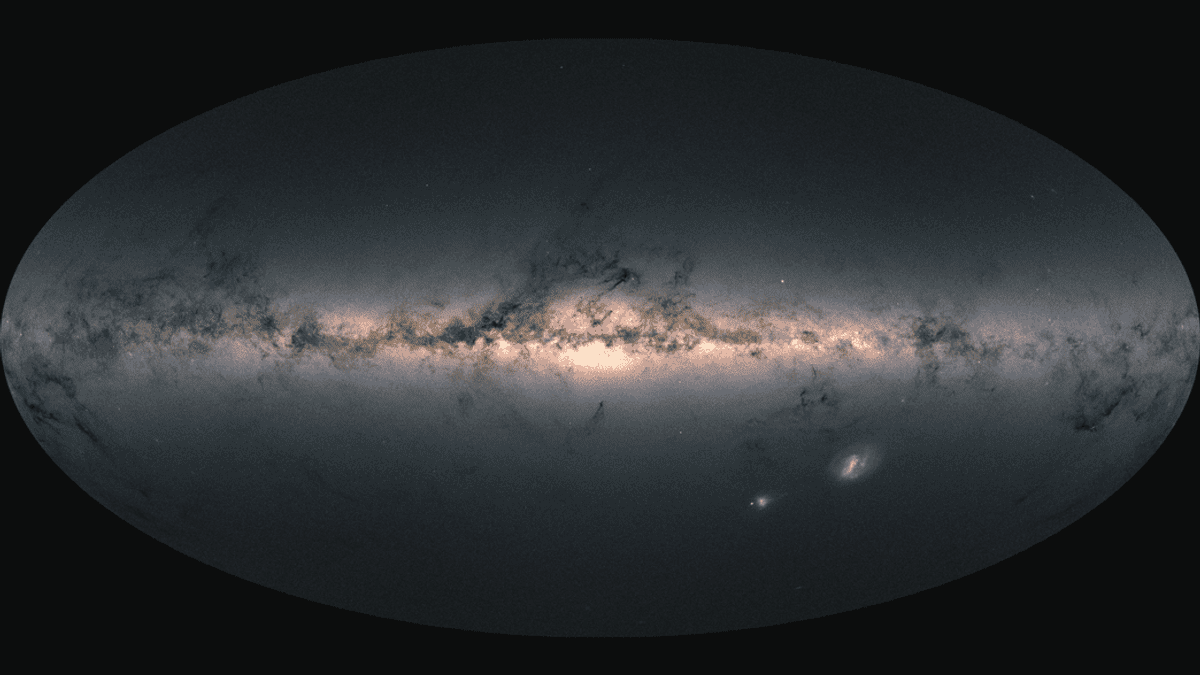
Essentially the most detailed map of the Milky Method remains to be being constructed, however you’ll be able to take a look at its present and most full iteration but. Gaia is a mission run by the European House Company to catalogue the huge database of stars that make up our galaxy.
Noticed by IFLScience (opens in new tab), The ESA has launched the third information drop from the Gaia mission (opens in new tab), and it comprises greater than sufficient area information to assist make any earthling really feel a lot, a lot smaller.
The earlier launch of information was again in December 2020. It lined data on over 1.8 billion stars. This contains particulars just like the place, actions, brightness, and colors of those stars. The third data launch which occurred simply yesterday, builds on this information a lot additional.
Not solely do we’ve got the classifications of stars, however Gaia additionally supplies even additional information just like the chemical elements which might then be used to work out even additional particulars. These particulars even let Gaia differentiate between stars not initially fashioned within the Milky Method, however had been reasonably absorbed because the galaxy grew.
“Our galaxy is a lovely melting pot of stars,” explains Dr Alejandra Recio-Blanco of the Observatoire de la Côte d’Azur in France, and member of the Gaia collaboration.
“This variety is extraordinarily essential, as a result of it tells us the story of our galaxy’s formation. It reveals the processes of migration inside our galaxy and accretion from exterior galaxies. It additionally clearly reveals that our Solar, and we, all belong to an ever-changing system, fashioned because of the meeting of stars and fuel of various origins.”
The Gaia information seems to be nearly like an image of the Milky Method zoomed out, however is as a substitute mapped out positions of the celebrities, planets, asteroids, and even mud within the system. It can also recognise and distinguish binary stars, of which it is noticed round 813,000 in our galaxy. It is also seen far more planets than there will be in Starfield (opens in new tab). The knowledge and sensors are even ok to determine the adjustments which have occurred inside a star by checking for variations in brightness.
Gaia can be choosing up information it wasn’t even designed for. Due to the ability of those scans it has even detected and catalogued starquakes, that are motions on the floor of a star. Hundreds of stars have had their starquakes noticed, which might educate us much more in regards to the burning balls of fuel and their inner workings.
You may freely browse the Gaia missions information on the official web site, however it’s fairly daunting stuff. That is all dense information reasonably than fairly area photos and it is extremely in depth. Whereas it could present tonnes of data within the appropriate fingers, aside from marvelling at its existence it is all a bit past me. There are some tutorials to assist, for the additional decided trying to unravel the mysteries of our galaxy.

