Intel has outlined some spectacular objectives for its next-gen Meteor Lake CPUs to get any PC gamer salivating. These embrace delivering better than 20% sooner clock speeds for a similar energy as Alder Lake makes use of at this time, and using EUV (excessive ultraviolet) lithography for a a lot improved Intel 4 course of node.
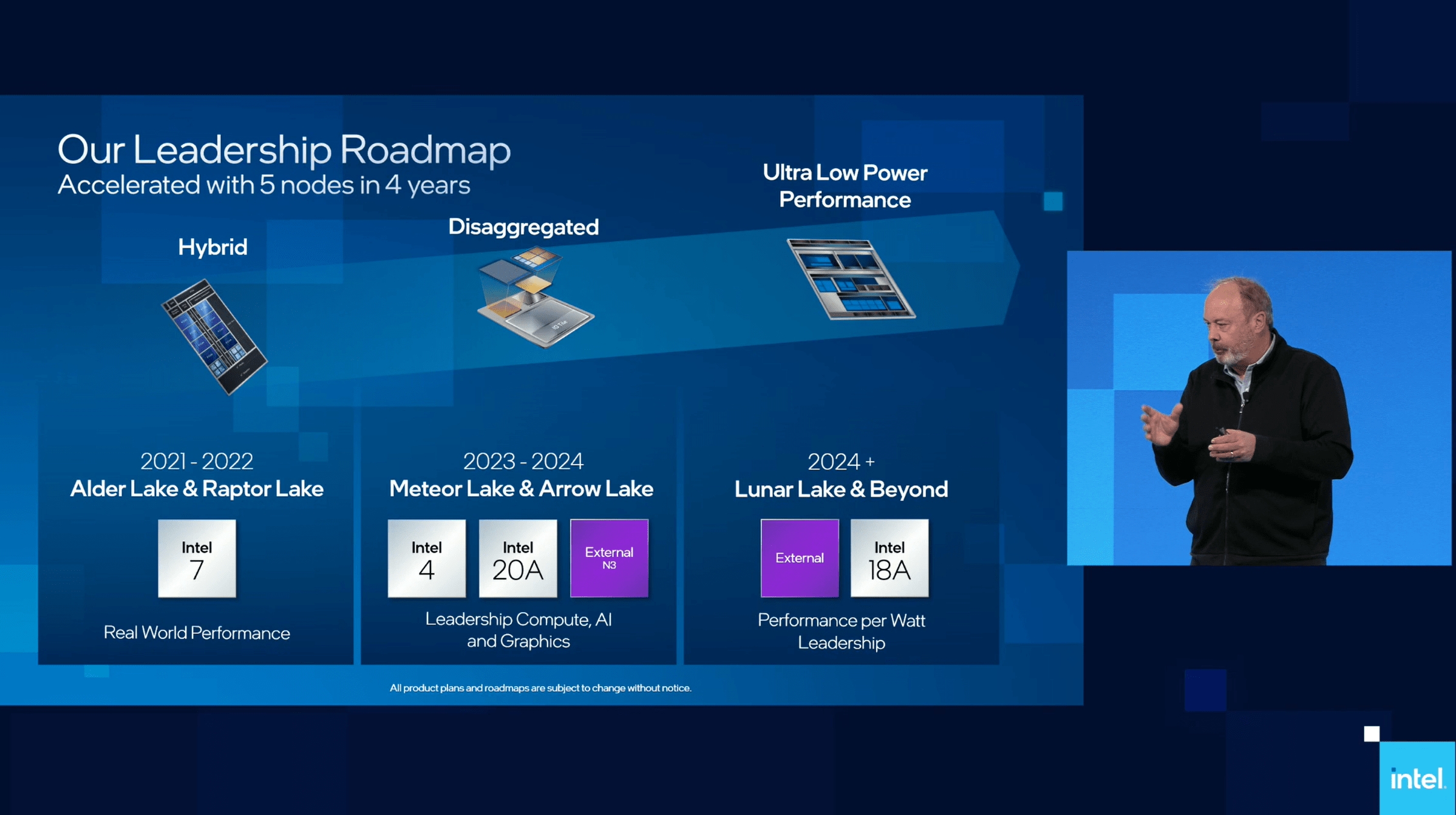
The Meteor Lake processor era hasn’t obtained an official launch date but, however it’s anticipated to reach later in 2023 if all goes to plan. This would be the first of Intel’s client CPUs to truly use a chiplet design, connecting compute, GPU, and SoC dies by way of its Foveros packaging course of. It is not the subsequent chip era anticipated from Intel—that is Raptor Lake, a refresh of the present Alder Lake processors—however it’s the subsequent one after that.
That hasn’t stopped a few of the juicy particulars from popping out about this future chip era, nevertheless, as Intel has elaborated extra on this upcoming chip launch on the 2022 IEEE VLSI Symposium.
Many of the following data was included in slides taken from the present by Twitter account @phobiaphilia (opens in new tab) and later reported by ComputerBase (opens in new tab), however the cited tweets have since been deleted.
Nonetheless, it seems as if Intel is urgent on as deliberate with Meteor Lake. Meteor Lake would be the first client CPU constructed utilizing the Intel 4 course of node, and with that new course of comes a goal of greater than 20% larger frequencies for a similar energy as the method node utilized by current twelfth Gen chips, Intel 7.
In idea, that ought to see fairly a step up in efficiency with out the need to extend processor energy necessities even additional. But I’d nonetheless count on the subsequent few processor generations will improve energy calls for. Intel shall be pushing to maximise its efficiency versus the strict competitors over at AMD, and effectivity is often the very first thing to exit the window within the pursuit of upper efficiency. That is not solely in CPUs however in GPUs, too.
Intel has already confirmed Meteor Lake with a 5–125W Watt thermal vary, however that does not essentially imply that is the height wattage that we’ll see these chips run at on desktop.

One other advantage of the Intel 4 course of node embrace 2x extra space scaling, which is able to see Intel squeeze the identical circuitry right into a a lot smaller footprint than earlier than. That is helpful for an entire method of issues, however will provide the flexibility to both enhance effectivity with smaller chips or stuff extra efficiency onto a single die than ever earlier than.
An image of the Meteor Lake compute die up-close from the symposium exhibits six massive cores alongside eight small cores. In different phrases, and assuming equivalent nomenclature to Alder Lake, a 6+8 die with six Efficiency-cores (P-cores) and eight Environment friendly-cores (E-cores). This makes a change from the two+8 design beforehand proven off by Intel.
This compute die is not alone on the chip, nevertheless. It is joined by a graphics die, an SoC die, and an IO die. The precise format of which could match the slides proven, or maybe extra doubtless take a type nearer to the take a look at chips shot by CNET (opens in new tab) just a few months again.
(opens in new tab)
This multi-die method is made potential by the Intel 4 course of node’s compatibility with packaging applied sciences akin to EMIB and Foveros. EMIB is Intel’s interconnect know-how, and we all know the corporate plans to make use of ’tiles’, or chiplets, in its future CPU and GPU designs extensively. Foveros is Intel’s know-how for packaging dies on prime of each other.
We all know these applied sciences shall be utilized by Intel in producing a Meteor Lake CPU with a big Intel Arc graphics element stacked on prime sooner or later or one other. What Intel’s Raja Koduri refers to as (opens in new tab) ” discrete graphics-class efficiency with the effectivity of built-in graphics.” That is in all probability an entire completely different kettle of fish to the extra conventional CPUs we’re at this time, nevertheless.
Nonetheless, it is fairly the prospect for PC gaming, particularly for gaming laptops and probably extra compact machines. Usually EMIB and Foveros assist will open the door to loads of thrilling prospects, and it is not simply Intel that is seeking to bigger stacked chiplets—AMD was the primary to roll a chip utilizing stacked cache to the desktop with the AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D (opens in new tab).
In the end, Intel actually would not need wish to be overwhelmed to the punch by its competitors. Offering Intel delivers on its guarantees right here, although, the corporate could possibly be see itself really again at a extremely aggressive degree with the likes of TSMC and AMD.

